Scientists have discovered that by harnessing the natural transport of electrons within plant cells, it is possible to generate electricity as part of a green, biological solar cell. The researchers believe that their technique could pave the way for the creation of sustainable, multi-purpose green energy technologies in the future.
Also read: New battery technology may boast capacity by four times
The electrons are naturally transported as part of biological processes in all living cells, from bacteria and fungi to plants and animals. By introducing electrodes, the cells can be utilized to generate electricity that can be used externally. Previous research had created fuel cells using bacteria but it required constant feeding. This new approach uses photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, to generate current.
Also read: Micrometeoroid strike on Russian spacecraft may force astronauts to stay for full year
During this process, light drives a flow of electrons from water that ultimately results in the generation of oxygen and sugar. This means that living photosynthetic cells are constantly producing a flow of electrons that can be pulled away as a “photocurrent” and used to power an external circuit, just like a solar cell.
Certain plants — like the succulents found in arid environments — have thick cuticles to keep water and nutrients within their leaves. Yaniv Shlosberg, Gadi Schuster, and Adir wanted to test, for the first time, whether photosynthesis in succulents could create power for living solar cells using their internal water and nutrients as the electrolyte solution of an electrochemical cell.
Also read: Rare green comet loses part of its tail to solar storm
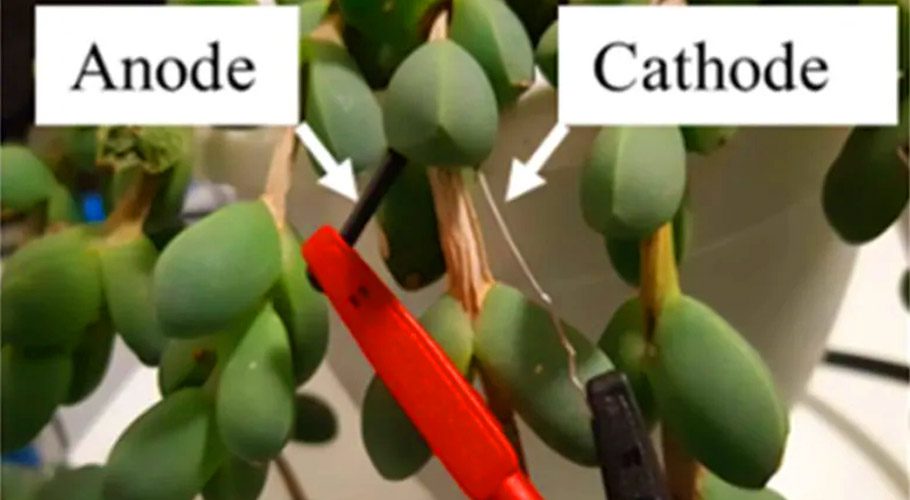
The researchers created a living solar cell using the succulent Corpuscularia lehmannii, also called the “ice plant.” They inserted an iron anode and platinum cathode into one of the plant’s leaves and found that its voltage was 0.28V. When connected into a circuit, it produced up to 20 µA/cm2 of photocurrent density, when exposed to light and could continue producing current for over a day. Though these numbers are less than that of a traditional alkaline battery, they are representative of just a single leaf.
Also read: AI set to takeover religious teachings
Previous studies on similar organic devices suggest that connecting multiple leaves in series could increase the voltage. The team specifically designed the living solar cell so that protons within the internal leaf solution could be combined to form hydrogen gas at the cathode, and this hydrogen could be collected and used in other applications. The researchers say that their method could enable the development of future sustainable, multifunctional green energy technologies.